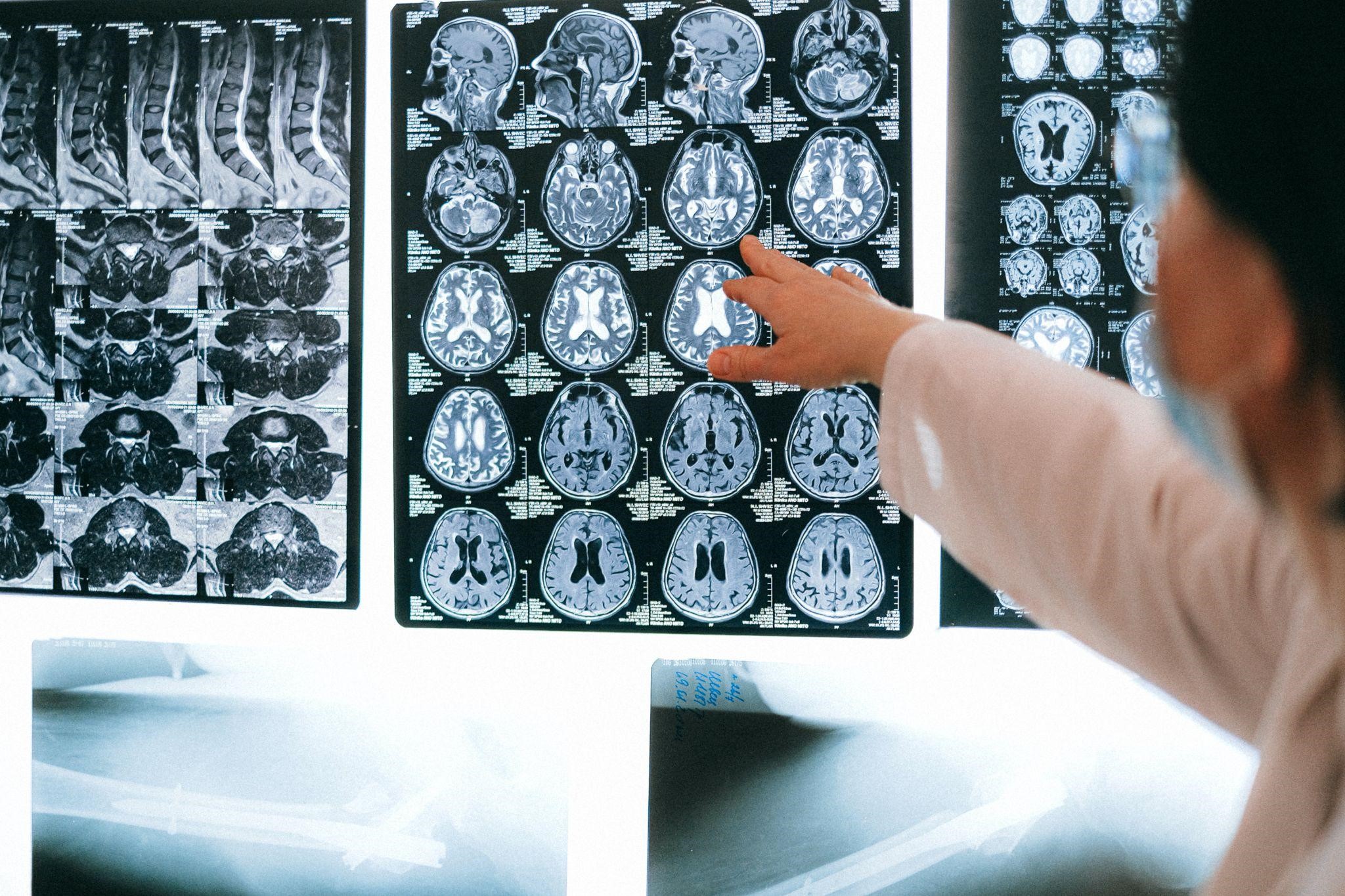
Radiology technologists monitor patients for exams, position them correctly, operate the equipment, and use essential radiology expertise and knowledge to limit the patient’s radiation exposure.
The titles “radiologic technologist” and “radiology technician” refer to the same profession and are usually interchangeable. Additional synonyms for these terms include:
- Radiographer
- Radiologic tech
- Radiology technologist
- Radiologic technician
- Radiology tech
- Rad tech
There are various paths to becoming a radiologic techologist. However, some steps may be more advantageous than others in the long run.
For example, radiologic technology aspirants may attend colleges with radiology programs to boost their career prospects.
This article discusses what radiologic technologists do, how aspirants can become official radiologic technologists and the necessary skills for the job.
This write-up also provides information on radiologic technologists’ average salary.
How to Become a Radiologic Technologist
Below are the typical requirements you must meet to be a radiologic technologist.
Education Requirements
People interested in becoming radiologic technologists should be proficient in math and physics, possess interpersonal skills, and can think critically.
High school courses in anatomy and physiology, computer sciences, biology, chemistry, physics, and algebra are all excellent options for aspiring radiologic technologists.
The steps below summarize the prerequisites and requirements for working as a radiologic technologist:
- Earn a secondary (high school) diploma, or pass the GED (General Educational Development) test.
- Obtain a diploma, such as an associate’s, a bachelor’s, or a certificate in the radiologic technology program.
- Get certified. Most states and employers require credentials from an accredited program.Sometimes, pursuing a career in radiologic technology may necessitate passing a state licensure exam.
- Consider specialization. Taking X-rays is a typical entry-level task for those starting a career in radiologic technology.Still, securing specialty certification may help a radiologic tech qualify as a sonographer or mammographer.
Degrees and Programs
Most companies and medical imaging centers expect radiologist technologists to have a formal educational certification from an accredited college-based or hospital-based training program.
Degree courses in radiologic science or radiologic technology may focus on specific course subjects:
- Human anatomy, pathology, and physiology
- Radiation physics
- Radiation therapy treatment planning
- Patient care
- Medical imaging procedures
- Radiographic pathology
Coursework
An A.A.S. (Associate of Applied Science) in Radiologic Technology is excellent educational training for people who want to be at the forefront of technology of patient care and technology.
An A.A.S. in rad tech is typically a 75-hour degree split into two components introductory courses and professional radiologic coursework.
Obtaining an A.A.S. in rad tech may entail the following steps:
1. Applying for and completing prerequisite coursework.
The first step is to find a university that offers a biological sciences-focused degree program.
You may have to pay application fees and provide transcripts from high school and college.
Completing prerequisite coursework in English, basic anatomy, physiology, healthcare, medical terminology, and psychology may be necessary.
2. Attending the university’s radiologic technology degree program.
Students may qualify for admission to the college’s radiologic technology program after completing the prerequisite coursework.
After acceptance into the program, students must pass many screenings and exams before applying for jobs as healthcare providers.
3. Finishing the coursework for professional radiologic technology
Students may complete their remaining college credits, typically in lock-step fashion. With this option, the knowledge acquired in one subject is directly relevant to the next.
Licensing and Certification
People applying for a radiologic technology license must be degree holders of accredited programs, according to the BLS (Bureau of Labor Statistics). Additionally, the candidate must pass a state certification exam or obtain certification from an accreditation body.
Radiologic technologists can choose from various specializations.
The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) offers certificate programs for radiologic technologists.
For MRI technologists, certification is available through the ARRT and the American Registry of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techs (ARMRIT).
You can learn more about the licensing requirements for radiologic and MRI technologists by contacting the state’s health board.
Radiologic Technologist Job Description
Radiologic technologists work alongside physicians to treat patients of all ages. Typical tasks and obligations at work include:
- Evaluating, assessing, and assessing patients
- Putting patients in the proper position for diagnostic imaging procedures
- Taking care of patients while performing imaging procedures
- Educating patients on the testing procedures
- Keeping up with and using knowledge of radiation safety and protection procedures
- Storing patient records up to date, organizing photos, ensuring photo clarity, and sending photos to the doctor
- Performing procedures or helping a licensed practitioner perform them
- Cleaning and maintaining imaging equipment according to best practices
How Much Do Radiologic Technologists Earn?
The BLS reported that radiologic technologists and technicians in the United States earned an annual salary of $61,370 in May 2021.
In May 2021, the leading sectors paid their radiologic technologists and technicians an average of the following amounts per year:
| Federal government, excluding postal service | $71,530 |
| Outpatient care centers | $67,240 |
| Medical and diagnostic laboratories | $62,410 |
| Hospitals, state, local, and private | $61,670 |
| Physicians’ offices | $59,500 |