Staying Digitally Safe
Internet-based services and goods, tools, and technologies have changed the way we used to work and live. They have made life easier for us and made every element, including our professional and personal lives, more convenient. But since every coin has two sides, technology has also brought up several security issues and dangers that could completely ruin both, professional and personal lives.
Millions of dollars have been lost by businesses, along with customer confidence and their reputation in the market. Similarly, people have experienced fear due to threats and crimes related to exposed personal information.
Since hackers are also experienced professionals, their hacking techniques are always changing. Some employ their talents to commit crimes, while others work for organizations to combat malicious hackers. And it’s important to be aware of developments in the cybersecurity sector as well as the different sorts of attacks and hackers if one wants to protect self and the company from them.
What is Hacking? Which are the Common Types of Hackers?
Exploiting security flaws to obtain unauthorized access to any smartphone, computer, network system, or tablet is known as hacking. Hackers exploit and break into the victim’s system without permission and obtain a wealth of personal information, including personal and financial data and passwords.
In the hacking world, the hackers are known as ‘white hat hackers’ or ‘ethical hackers’ since they use their expertise to prevent the theft of confidential information rather than to exploit systems or access the victim’s system. Some hackers use their expertise for retaliation, financial gain, or even just for amusement. Here are some typical hacking methods that one should be aware of to either prevent self from getting hacked or at the very least take some preventive action.
Top Common Hacking Techniques seen in 2022 are as below
Precisely, hacking is all about simplicity and believability. When hackers seek to steal someone’s priceless personal data, they get resourceful. They may pose as someone’s bank, impersonate antivirus software, or even warn of a problem that doesn’t exist.
The best way to defend oneself is to be informed, so read on to learn about the most popular hacking methods, why people fall prey to, and how to avoid being a victim.
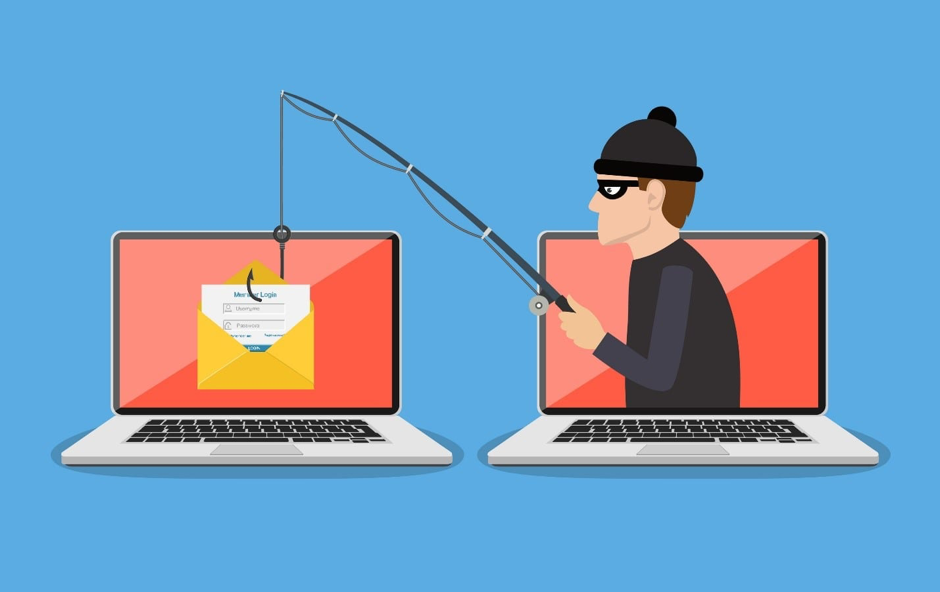
1. Phishing & Social Engineering
The goal of social engineering is to obtain personal information from a possible victim, who is usually an employee of the targeted company, generally by pretending to be someone they can trust.
Phishing emails are a common sort of social engineering bait when an actor (threat) sends a message that appears to be from someone the user knows. This message pretends to be helpful while asking users to click and download a malicious attachment. The user’s computer could become infected if such infected file is downloaded, permitting the threat actor access to occasionally the user’s entire network.
Solution: Remind your staff or ensure the user himself should never send sensitive company information over email. Think twice before clicking on any attachments and learn how to spot email fraud.
2. Missing Security Patches
With the growth of the hacking scenario, security tools may turn old. To protect against novel dangers, they need to be updated very often. Nevertheless, some users neglect update notices or security updates, giving hackers permission to attack. Not only antivirus software needs to be patched.
Solution: The security patches are immediately available, so ensure to update all of the antivirus programs and software regularly. Take into account vulnerability assessments to make sure that the most obvious vulnerabilities are found and fixed first.
3. Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDOS)
This hacking method targets shutting a website down so that users are unable to access it or use it for business reasons. Attacks called (DoS) comprise flooding the target’s server with a lot of traffic. The frequency and volume are so great that the server becomes overloaded with excessive requests than it can process. In the end, the user’s server fails, taking the website down with it.
A Distributed Denial of Service threat, which is a coordinated attack on many websites or servers using multiple computers at once, may target larger corporations and bring down numerous internet assets.
Solution: To safeguard a company from a site takedown, try DDoS mitigation services or a cloud protection service. To confirm that the selected protection strategies are successful, take into account product claims testing and external network penetration testing.
4. Malware-Injecting Devices
Hardware can be used by cybercriminals to install malware on the computer. For example, once the infected USB is inserted into the computer, hackers will have easy remote access to the device.
Users’ entire company might be in danger if only one employee offers a USB drive that is affected by malware. Moreover, devious hackers are also injecting malware using wires like mouse cords and USB cables.
Solution: Inform the staff or stay alert about physical malware injection techniques and advise them to pause and consider their actions before plugging in a mysterious drive or cable.
5. Cracking Passwords
Hackers may get anyone’s login details in multiple ways where undetected software that was involuntarily downloaded by a ‘social engineering’ target scam records keystrokes that the actor (threat) can use at their will. This comprises the affected machine saving passwords and usernames as they are fed by the user.
Solution: Use a password management program to save all the business credentials safely. These programs frequently auto-generate lengthy passwords with a variety of characters that are challenging for hackers to brute force guess—and autofill for the staff members to provide them quick access to their programs. To protect data from hacking tactics that are not picked up by automated scanning, think about looking into multi-factor authentication and encryption methods.
6. Keylogger Attack
‘Keylogger attack’ is a hacking method that uses software or hardware that legally records keystrokes on the keyboard. In Australia, Formbook is the most prominently used software for info-theft, which accounts for 3 percent of all recorded cyber incidents.
The term “keylogger” refers to both a program (log file) that records keystrokes and sequences as well as physical equipment that targets smartphone sensors, keyboards, electromagnetic emissions, and more. User passwords and other private information can easily be recorded in this way without the user’s permission or knowledge.
Solution: Use keylogger detection; select an antivirus program that offers this level of security, together with a password manager. Use VPNs and secure connections. When possible, enable two-step verification.
7. Clickjacking Attacks
A typical hack, often referred to as UI redress, involves hiding the UI that the victim is thought to click. Without the victim’s cooperation or knowledge, the hacker diverts their clicks away from the intended page and onto another. The majority of hijacked clicks result in advertisements on a hacker’s website, which brings in advertising money. However, hijacked clicks can also be used to manipulate harmful links and spread malware or steal data.
Solution: Add a few lines of JavaScript to the head section of the susceptible website’s page to use frame-busting techniques. Ask the browser to prevent any attempts to embed an I-frame on the website (X-frame HTTP Header settings). Use certain Content Security Policy instructions. Utilize cookies’ same-sit plugin property.
Conclusion
Bulk crucial information is widely available online. Individuals with a keen mind can pick things up quickly and adjust. What distinguishes hackers is their motivation for hacking. Hackers are harmful since the information is exploited to damage people or governments or for personal gain. Hacker attacks can take many different forms depending on the company. The degree and kind of attack depend on how successfully the hackers can exploit the security mechanism. So, one must essentially know the common hacking as well as the prevention techniques to stay safe, digitally.